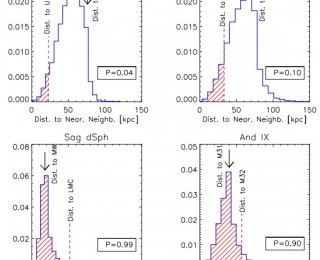
Too many galaxy pairs in the Local Group?
Pairs of dwarf galaxies in the Local Group are much more common than what expected from N-body/semi-analytic models of galaxy formation.

Pairs of dwarf galaxies in the Local Group are much more common than what expected from N-body/semi-analytic models of galaxy formation.
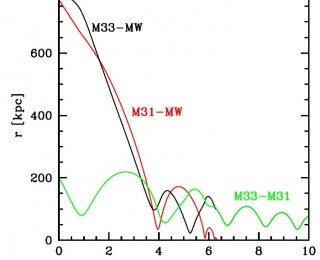
HST measurements of stellar proper motions in M31 reveal that the Andromeda galaxy is in radial (head-on collision) orbit towards the Milky Way. The huge strike will happen 4 billion years from now according to the simulations. It will likely affect also the environment of the Sun and the location of the solar system.
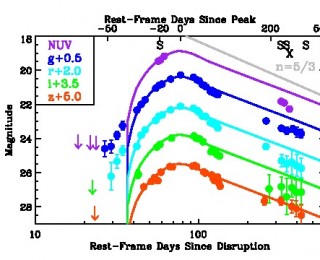
A luminous ultraviolet-optical flare of radiation reveals the tidal disruption of a star wandering on a quasi-parabolic orbit in the vicinity of a supermassive black hole. This is the most direct evidence yet of a supermassive black hole shredding a star that swirled too close.
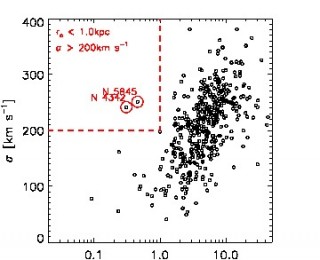
NGC 5845 is a nearby compact galaxy, more similar to the recently discovered high redshift z~2 compact galaxies than to its low-redshift mates. This makes it rare and interesting, as its structure and kinematics can be studied much better than is possible at high redshift. The analysis reveal a prominent rotating stellar disk, suggesting that similar structures could be present in high-redshift compact galaxies too.
Dark matter profiles of dwarf galaxies in high resolution hydrodynamical simulations are compared with observations. A physically motivated energy feedback from Supernovae generates gas outflows which are able to remove efficiently large fraction of gas from the inner regions of the galaxies, thus forming central cores and alleviating the “core-cusp problem”.