10.(Tie with 9) Stellar and Dark Matter Mass tell Galaxies When to Stop Forming stars
- Title: New constraints on the evolution of the stellar-to-dark matter connection: a combined analysis of galaxy-galaxy lensing, clustering, and stellar mass functions from z=0.2 to z=1
- Authors: A. Leauthaud, J. Tinker, K. Bundy, et al.
- First Author’s Institution: Lawrence Berkeley National Lab, Berkeley
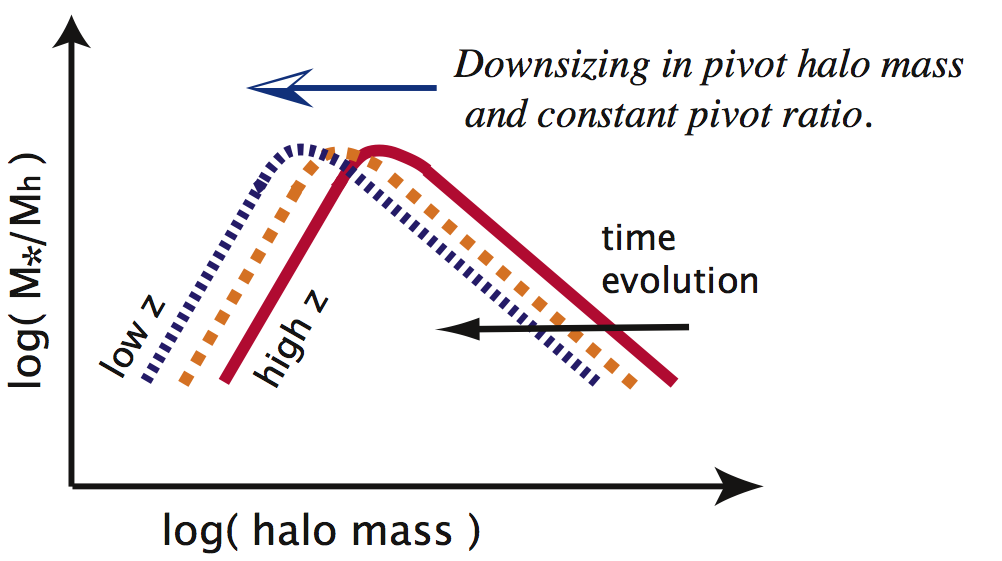
Why it is important: The observed bimodal color distribution of galaxies– either blue and star forming like our own spiral Milky Way galaxy, or ‘red and dead‘ (usually) like ellipticals– leads us to believe that something causes galaxies to evolve from gas-rich to gas-poor. Here, the authors look for trends in large galaxy samples to catch this evolution in the act.
Previous: (# 11) Dark Matter core, nothing more! How to Mess With the Dark Matter in Dwarf Galaxies

Hi Betsy:
Just a note– it looks like the arXiv link that you have on the first page of this article does not link to the title you provide.
The link looks like it goes here:
http://arxiv.org/abs/1106.0499
“How supernova feedback turns dark matter cusps into cores”
instead of here:
http://arxiv.org/abs/1107.1261
“Keck Spectroscopy of Faint 3<z<8 Lyman Break Galaxies:- Evidence for a Declining Fraction of Emission Line Sources In the Redshift Range 6<z<8"
Thanks,
Dave
Ah, actually the links are just switched–
Thanks,
Dave
Thanks Dave! The links are now fixed.
Fascinating articles! But counting citations seriously distorts what astronomy is about. Because most young astronomers today work in observational cosmology, 10/12 papers are on that topic, the most glamorous frontier. But 10/12 of the most significant new papers of 2012 (selected some other way) paint a certainly much broader canvas, and reflect the amazing scope of astronomical research!
Only the search for new planets (another glamour topic) and new calculations of the evolution of rotating stars in the HR diagram (a classic issue in stellar astronomy) penetrated the top twelve. So much more was missing!
Nonetheless, an interesting citation poll.
Hi, I think the mass-to-light ratio of a low-mass star is higher than that of a high-mass star. In addition, the Salpeter IMF has more low-mass stars than the Kroupa and Chabrier IMFs.
I think that the article in astrobites has more detail introduction:
http://astrobites.com/2012/02/16/the-imf-is-not-universal/
Yes, I had the mass-to-light ratio section entirely backward; this is now corrected (and consistent with the linked astrobite). Thank you!!