by Shang-Min Tsai | Aug 28, 2017 | Daily Paper Summaries
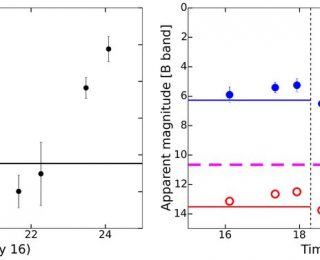
Besides our Earth, lightning has also been observed on Jupiter and Saturn, identified by the optical flash or the radio signal. In today’s bite, the authors take an even further step. They analyze whether lightning can explain the mysterious radio signals from the exoplanet HAT-P-11b.
by Shang-Min Tsai | Jul 21, 2017 | Daily Paper Summaries
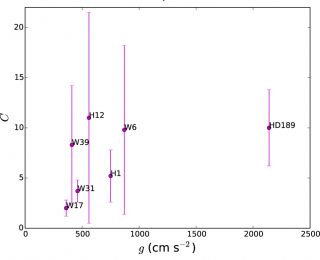
In a clear, cloud free atmosphere, the difference in transit radii between the line center and wing of sodium can be theoretically calculated. By measuring the actual difference in transit radii between the line center and wing (Δ Robs), the author constructs a dimensionless index (C) for the degree of cloudiness as the ratio of Δ R and Δ Robs. For an entirely cloud-free atmosphere, Δ R equals to Δ Robs hand C = 1. Very cloudy atmospheres have C Gt 1. This cloudiness index is independent of the spectral slope, with the caveat that it is limited to planets with sodium or potassium line detections.
by Shang-Min Tsai | Jun 23, 2017 | Daily Paper Summaries
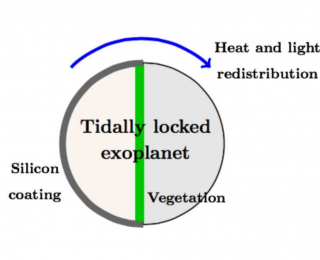
Alien civilizations might build large-scale arrays of solar cells to harness energy from their host star. Such coverage of photovoltaic materials have distinctive and probably detectable spectral features, similar to the “red edge” of vegetation.

by Shang-Min Tsai | Jun 12, 2017 | Daily Paper Summaries
Again, out of surprise, ammonia is not well-mixed, as predicted by the equilibrium chemistry. There is an equatorial plume lifting ammonia up and descending at higher latitude, resembling a Hadley cell on Earth.
by Shang-Min Tsai | May 5, 2017 | Daily Paper Summaries
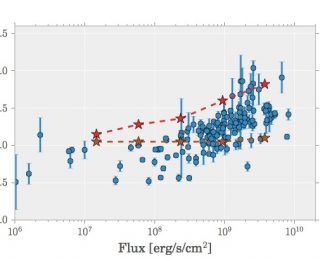
Hot Jupiters passively cool down and contract after formation. Standard models can predict their thermal history and how much their radii should contract up to present time. Yet the observed radii (e.g. through transit) are larger than prediction. The possible solutions to this problem can be categorized into two types: (I) constantly injecting energy into the interior (II) delay the cooling process. (I) includes downward transport of kinetic energy, or energy dissipated by the interaction with the magnetic field (ohmic dissipation). Enhanced opacities are also proposed to reduces the cooling rate, which belongs to (II). However, the above mechanisms are either not robust or restricted to fine-tuned parameters. So the radius anomaly remains an intriguing open problem.





