Cosmic reionization: Who is to blame?
What caused the universe to shift from neutral to ionized as it expanded and cooled? Today, we examine clues that indicate it could have been the result of rapid star formation from the earliest galaxies.

What caused the universe to shift from neutral to ionized as it expanded and cooled? Today, we examine clues that indicate it could have been the result of rapid star formation from the earliest galaxies.
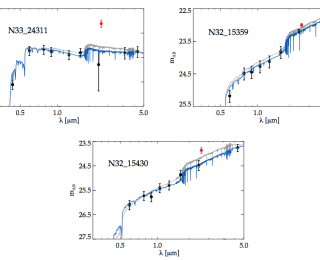
How do emission lines from nebulae affect broad-band photometry of high redshift galaxies?
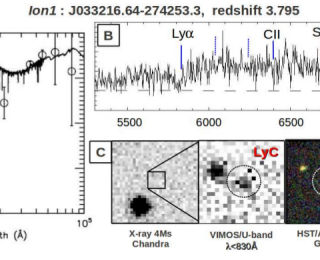
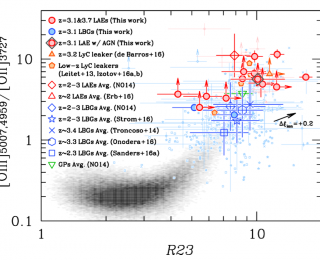
Any photon with a wavelength shorter than 912 angstroms (the Lyman limit) will ionize neutral hydrogen by raising the atom’s electron from the ground state to an unbound state at infinity. From measurements of quasar absorption spectra, we know that the reionization of the intergalactic medium from its previously neutral state (at redshifts greater than 7) to the highly ionized state we observe today was complete by redshift of ~7. However, we still do not know which sources were responsible for producing the ionizing photons.
Lensing occurs when the mass of a foreground object distorts and magnifies the light from a background galaxy or quasar, sometimes even creating multiple images. It probably isn’t a stretch to say that the neatest thing about lensing is that you can typically see two to four images of the same galaxy. But something else that’s cool is that these distant background objects are magnified, making it possible to study them in detail when otherwise they might not be seen at all: in this way, gravitational lenses act as natural cosmic telescopes.