- Paper title: Colors of a Second Earth II: Effects of Clouds on Photometric Characterization of Earth-like Exoplanets
- Authors: Yuka Fujii, Hajime Kawahara, Yasushi Suto, Satoru Fukuda, Teruyuki Nakajima, Timothy A. Livengood, Edwin L. Turner
- First author’s affiliation: Department of Physics, The University of Tokyo
As Ellie mentioned three weeks ago, the Kepler team has already announced the detection of 68 roughly Earth-size planet candidates. Although Kepler is not capable of conducting photometric or spectroscopic studies of the atmospheres of these worlds, future missions are being designed to achieve that goal. Assuming that we have acquired the spectrum of a distant terrestrial planet, what would it look like? Would we able to resolve surface features? More excitingly, would we be able to detect biomarkers in the atmospheres of alien Earths?
Summary
This paper is the second in a two-paper series that addresses the question of how a habitable Earth-like planet might appear in a future imaging campaign. In the first paper, the authors modeled the appearance of a cloudless Earth-like planet. In this paper, they improve their model by including temporally varying clouds and more realistic treatment of radiative transfer in the planet’s atmosphere. They also apply validate their model by comparing their synthetic light curves to actual Earth observations.
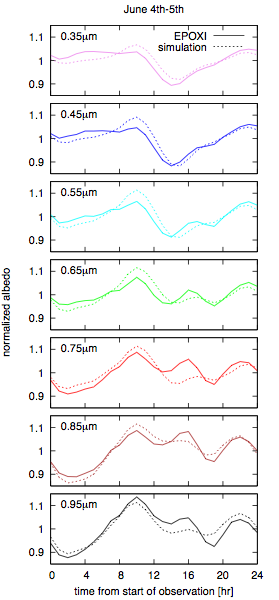
Comparison of the light curves of the simulated light curves (dashed) to the actual light curves obtained by EPOXI (solid). All curves were normalized by their time average. Figure 6 from Fujii et al.
Since we don’t yet have photometry of another Earth-like planet, Fujii et al. use observations of the Earth to develop the tools needed to investigate the surface properties of other Earth-like planets. In the first paper and in part of this paper, the authors produce synthetic light curves of the Earth by combining Earth observation data from the Terra and Aqua satellites with a radiative transfer model of the atmosphere. In Paper 1 the authors use a single scattering approximation, but in this paper they model radiative transfer more accurately by using the rstar6b code from Nakajima & Tanaka 1988.
Methods
To test their model, the authors compare their synthetic light curves with actual light curves of the Earth taken as part of the EPOXI mission. The EPOXI mission is using the spacecraft formerly known as Deep Impact to study extrasolar planets (EPOCh: (Extrasolar Planet Observation and Characterization) while it continues on its way to investigate another comet (DIXI: (Deep Impact eXtended Investigation). As shown in the figure at right, the simulated light curves match the EPOXI data quite well, so the authors feel confident in using their simulated light curves as the input for their surface characterization code.
Detecting Surface Composition
After validating their forward procedure to create light curves, the authors then work backwards to decompose the light curves into information about the planet’s surface properties. Using the albedo (reflectivity) models from the ASTER spectral library shown in the figure below, the authors determine the fraction of surface at each longitude band that is covered by snow, vegetation, ocean, clouds at three different heights, and two different types of soil. The inclusion of temporally and spatially varying cloud cover in this model is a major step toward realistically modeling Earth-like planets.
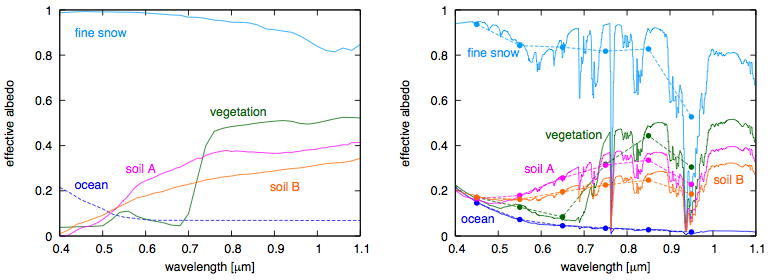
Effective albedo spectra for the five types of surface used in the model. Left: ASTER spectra without atmosphere. Right: Spectra with atmosphere but without clouds. The circles mark the averages over the EPOXI photometric bands.
Results
The authors find that their model does a good job recovering the existence of clouds and oceans on the Earth, but detecting the other components is more difficult. Although clouds and oceans could be detected using observations with a signal to noise ratio of 10, a much higher signal to noise ratio (~100) could allow for the detection of soil, snow, and vegetation. Of course, the authors point out that alien worlds might also have foreign surface components without Earth analogs, but this study is still an exciting glimpse into what planetary scientists may be studying twenty years from now.



This seems like a great idea fully deserving of being fleshed out. Can they only get albedo spectra from Earth because of EPOXI? It seems there has to be another way to acquire albedo spectra from other bodies without EPOXI-like crafts orbiting their surface. We could use that information to create a whole index of albedo-spectra from the rusty soil of Mars to the possible methane lakes of Titan.
I suppose it all comes down to the only answer being more exploration.
Ahem. What we WILL be studying twenty years from now 🙂 Unless the little green people come talk to us first.