Title: The Remarkable Similarity of Massive Galaxy Clusters from z~0 to z~1.9
Authors: Michael McDonald, Steve W. Allen, Matt Bayliss et al.
First Author’s Institution: Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, USA
Status: Submitted to The Astrophysical Journal [open access]
Introducing…Galaxy Clusters and X-rays!
We have come a long way since the 1930s, when the words ‘galaxy cluster‘ were posited for the first time by Fritz Zwicky, in relation with the presence of dark matter in the Coma cluster. Developments in multi-wavelength astrophysics have allowed us to probe different components of a cluster with different telescopes. For example, star-forming galaxies of galaxy clusters are observed using optical telescopes because starlight in these galaxies loves emitting photons with the roughly the same energy that we see from the sun. Some of these galaxies are super-red, have no star-formation and a ton of dust, that is best seen from infra-red and radio telescopes. Today’s story takes us to the intermittent space between different galaxies inside a cluster, called the intra-cluster medium (ICM) and its emissions.
The ICM of a galaxy cluster is filled with gas or plasma that comprise free electrons and protons. This medium reaches temperatures of the order of 10^7 to 10^8 K, that emits light in the form of X-rays. This happens due to a phenomena called free-free emission of electrons, or Bremsstrahlung. X-ray observations of galaxy clusters are a crucial element in understanding how the cluster gas evolves with time, and how they influence the formation and evolution of massive galaxies in clusters. Moreover, the effect of active galactic nuclei (AGN) that heat up cluster environments after firing up from individual member galaxies can also be analyzed through X-ray studies, using telescopes like XMM-Newton and Chandra.
Looking for Distant Galaxy Clusters
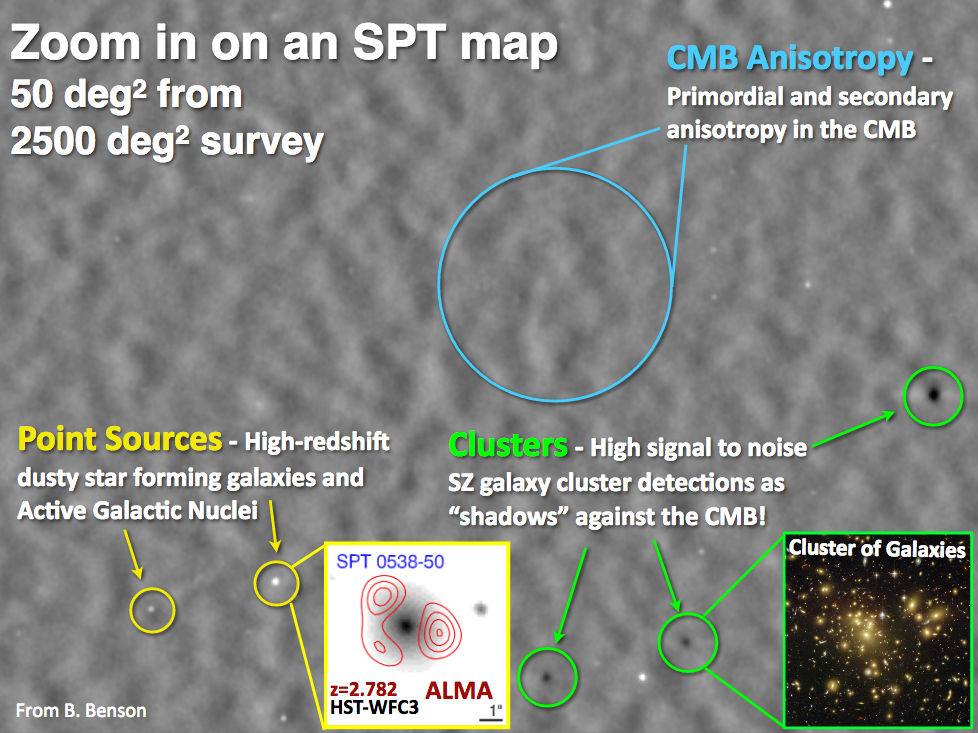
Fig 1. Picture of an SPT Cosmic Microwave Background map (created by Bradford Benson at Fermilab and University of Chicago, USA). This is a small patch of 50 sq. degrees with CMB anisotropies seen clearly. Small bright point sources are dusty galaxies that come out in these maps. Similarly, the dark spots are shadows on the CMB caused by inverse-comptonization of CMB photons by galaxy clusters.
This is easier said than done. We know a lot about close-by galaxy clusters by pointing an X-ray telescope to the sky, but finding X-ray emitting clusters that are extremely far-away is a tough job. This was made easy by the advent of sub-mm (or Cosmic microwave background (CMB)) telescopes, like the South Pole Telescope (SPT) or Planck. These telescopes discover galaxy clusters that cast a shadow on the background CMB, by a phenomena called the Sunyaev-Z’eldovich effect (look at this bite for details!) This makes cluster detection in CMB telescopes a distance (or redshift) independent activity, that gives us a better look at far away clusters.
Let’s make this slightly easier on us. If I was to summarize my chain of thought in the last two paragraphs, I would do so with the following steps:
Step 1: Study the CMB and look for shadows in the maps. These shadows are galaxy clusters that are distorting the background CMB light.
Step 2: Use an X-ray telescope to point to these shadows – you will see the X-ray ICM gas of these clusters.
Step 3: Make a list of these clusters, and study the X-ray ICM gas as a function of their distance, or redshift.
Step 4: Party.
Today’s paper is exactly that!
Evolution of the ICM
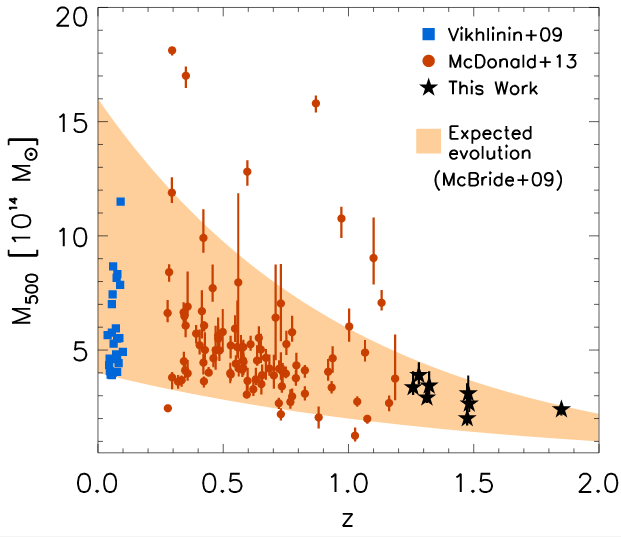
Fig 2. Plotted here is Mass of Cluster vs redshift for the clusters considered in today’s paper. The orange background is an evolution map, incorporating the physics of galaxy cluster evolution. This implies that clusters at high redshift (the black stars) could very well be the ancestors of nearby clusters (the blue squares) which are much more massive and fall within the orange band.
McDonald et al. present the first ever X-ray analysis of 8 galaxy clusters (with masses of ~2 to 4 x 10^14 solar masses) at redshifts greater than 1.2 that were detected with the SPT telescope, that add to the thermodynamic studies done by the same collaboration for low-redshift (or nearby) clusters. This allows them to discuss the evolution of cluster ICM from redshift 1.9 to redshift 0 i.e. from a time when the universe was 3 billion years old, to now! What they are looking for are signs of similarity between far away and nearby clusters. Not just looking alike, but whether distant clusters are younger versions of the nearby clusters. We call this property self-similarity – young less massive clusters accrete matter, cool down and evolve into massive clusters.
They find that centres of clusters, called cool cores, show no significant evolution in the density of the ICM gas when comparing far away clusters with close ones. As we go further out – about 20% of the ‘defined’ cluster radii – we see that far away and nearby clusters have self-similar densities. Based on their analysis, they propose a scenario where the cool cores formed at redshifts > 1.5 and their size, mass and density roughly remained constant. The rest of the cluster around them merrily continued accreting matter, and grew in their size and mass. This is possible if there is a gigantic AGN at the centre of these clusters, that is reheating all the cool gas that would have fallen to the centre of these clusters. This cooling and reheating seems to be tightly regulated, just like a thermostat on a fixed temperature. This explains the preservation of density around the cool cores, but not the rest of the massive cluster.
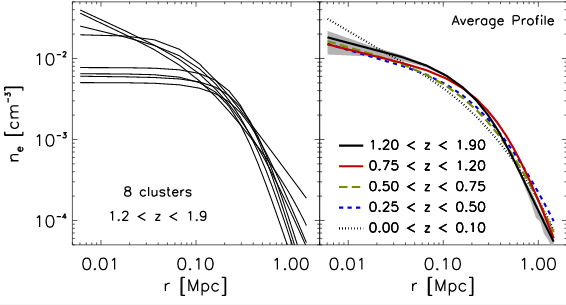
Fig 3. (a) Absolute gas density as a function of radius for the 8 new galaxy clusters studied in today’s paper. At low radii i.e. near centre of clusters, there is considerable difference in the density profiles, with a big scatter. As one goes outwards, the outskirts of the clusters look remarkably self-similar. (b) A similar result is seen when comparing clusters across different redshifts (or epochs).
Wait..what?!
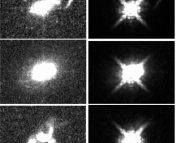
This is huge. The work in today’s paper indicates that far-away clusters could very well be progenitors to nearby clusters, if given enough time to evolve into massive structures. The cluster centres seem to stand the test of time, unfazed by the chaos around them. This is irrespective of how disturbed or relaxed the shapes of these clusters are, or how many galaxies are merging into these clusters.
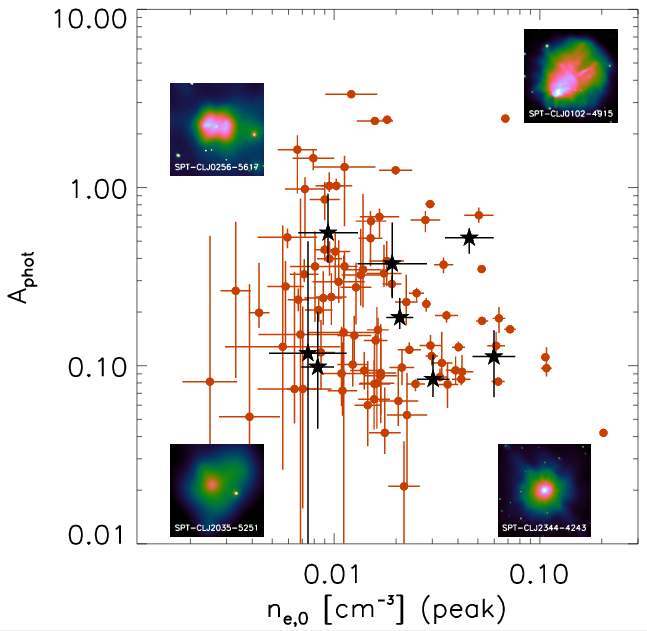
Fig 4. Photon assymetry (A, a tracer of disturbance in the clusters) vs electron density in galaxy clusters considered in today’s paper. The black stars are the 8 new clusters added to the analysis sample. This plot shows that there is no bias in the new sample, and the clusters span the typical range of these numbers, distributed uniformly.
A study like this makes us reach regimes where we can connect the physics of central cluster environments to its macro-surroundings, that we find so hard to replicate in hydrodynamical simulations at the moment. With the advent of new X-ray, CMB and optical telescopes, the precision with which we can make these claims only gets better!




Trackbacks/Pingbacks