Title: Observational constraints on the likelihood of 26Al in planet-forming environments
Authors: Megan Reiter
First Author’s Institution: UK Astronomy Technology Centre, Blackford Hill, Edinburgh
Status: Accepted to A&A Letters [open access]
We’re used to seeing aluminum in many aspects of our daily lives, from cooking and packaging to construction and electronics. On Earth, aluminum comes in the form of 27Al, which is its only stable isotope. However, aluminum can also exist in radioactive isotopes. 26Al is the most stable of the radioactive Al isotopes; it is produced inside massive stars as a result of nuclear fusion, and it can be injected into the interstellar medium through supernovae or stellar winds.
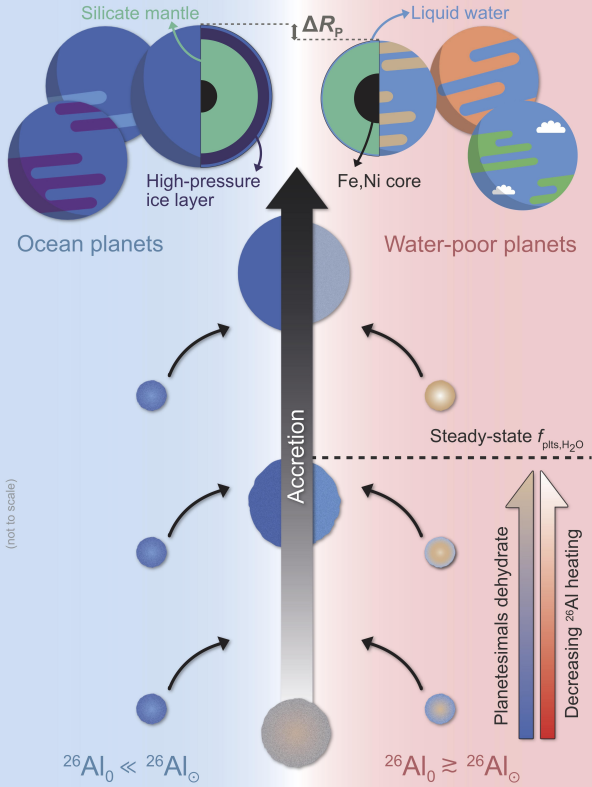
Recently, scientists have shown that the proportion of a terrestrial planet’s volume that is made up of water decreases with increasing abundance of 26Al in regions of planetary formation. The idea here is that heat released by the radioactive decay of this isotope plays a role in differentiating and dehydrating planetesimals, which leads to rockier and less-watery planets, as is shown in Figure 1.
We see no traces of the 26Al isotope on Earth currently; however, evidence from meteors suggests it was abundant in the early Solar System. Since the isotope has a comparatively short half-life when compared to the formation of the Solar System, this implies that the system was somehow enriched with 26Al during this time. Common theories of the 26Al enrichment of the Solar System involve interactions with supernovae or winds from Wolf-Rayet stars, and thus that it would be quite rare for a young, planet-forming system to be close enough to such an event to be enriched in this manner. As such, it has been argued that that the particular case of our Solar System represents a minority of planetary formation outcomes, and that water-rich planets should be the dominant type of terrestrial analogues.
However, the presence of abundant 26Al in planet-forming regions throughout the Galaxy may indicate that enrichment of young planetary systems is common, bringing into discussion the possibility that rocky, dry planets are more frequent than we think.
This paper compares the observed distribution of 26Al in the galaxy to the locations of star-forming regions in order to estimate the likelihood of 26Al enrichment during the formation of planetary systems.
26Al the Right Places
The Galactic distribution of 26Al is inferred from observations of the characteristic 1.809 MeV gamma-ray photons produced when 26Al undergoes radioactive decay. While the average emission throughout the Galaxy is 3-25 times lower than in the early Solar System, astronomers have found that the bulk of this emission is primarily associated with young star-forming regions. Furthermore, since 26Al is abundant in regions of ionized gas in the interstellar medium, and this gas is often produced by the stellar winds of high-mass stars, these stars must be the dominant sources of 26Al production.
In addition, observations of the Milky Way and other galaxies suggest that >50% of stars form in high-mass star forming regions or clusters. In the specific case of our Galaxy, these clusters coincide with regions of similar 26Al levels to the early Solar System. These two observations imply that a large fraction of the 26Al in the galaxy is made in star-forming regions by young stars. Since stars tend to form close together, this means the majority of stars form in 26Al-abundant regions, and thus are more likely to be exposed to, and enriched by, 26Al.
Foils in Our Designs?
Two specific factors can affect the probability that a young planetary system in these regions is actually 26Al enriched. The first one is the timescale of 26Al availability – 26Al has a half-life of “only” 0.72 Myr, so there may not be enough time for a coalescing planetary system to be significantly affected by the isotope. Observations of Galactic 26Al, however, show that high abundances persist for much longer than 0.72 Myr; this once again suggests that most of the observed 26Al is being continually produced by a population of massive stars, rather than single instantaneous events like supernovae. If these abundances are maintained for several Myr, they can last through multiple star-formation periods, thus increasing the likelihood that planetary systems in these regions are exposed to 26Al.
The second factor to consider is that simply exposing a new planetary system to 26Al does not imply that it will mix with the planet-forming material. For example, the expected ejection velocity of 26Al produced by winds and supernovae is >1000 km/s, which is too fast for it to coalesce within a protoplanetary disk. However, the observed bulk velocity of 26Al in certain regions of the galaxy can be much lower than this – in the Scorpius-Centaurus association, a nearby group of young massive stars, this velocity has been observed to be 137+-75 km/s, about an order of magnitude smaller than expected. Slower 26Al may mix more readily with planet-forming material, and thus enrich a greater fraction of these systems. The exact mechanism in which 26Al is incorporated into forming planetesimals is unclear, but the composition of meteors and extrasolar asteroids implies that it does indeed occur.
Conclusions
All in all, the authors suggest that high-mass star-forming regions of the Galaxy will be more conducive to 26Al enrichment, and thus more likely to have rocky planet formation, while low-mass regions which do not form stars massive enough to produce 26Al through fusion will be more likely to form water worlds.
In addition, these observations tackle the assumption that transient events like supernovae are the most significant sources of Galactic 26Al, and that the Solar System is particularly rare in this case. Instead, regular replenishment from massive stellar winds extends the abundance timescales of 26Al and allows for the majority of star-forming regions to be exposed to the isotope.
The paper concludes by acknowledging the need for future work to quantify the fraction of systems enriched with 26Al, and their ability and propensity to form rockier planets.
Astrobite edited by Isabella Trierweiler and Jason Hinkle
Featured image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt (IPAC)