Authors: Shany Danieli, Pieter van Dokkum, Roberto Abraham, Charlie Conroy, Andrew E. Dolphin, Aaron J. Romanowsky
First Author’s Institution: Department of Physics, Yale University
Status: Submitted to the Astrophysical Journal Letters, open access on arXiv
At the end of March last year, the Dragonfly team announced the discovery that galaxy NGC 1052-DF2 had almost no dark matter (see this Astrobite for more on the discovery). This announcement set off a flurry of responses, since the existence of an object like NGC 1052-DF2 has enormous implications for models of galaxy formation and behavior (see this Astrobite for a great summary of some of the initial responses).
To determine how much dark matter a galaxy has, you have to compare its stellar mass (which comes from estimating how many stars it has) and its dynamical mass (which comes from measuring how the contents of a galaxy are moving). Measurements of stellar mass and dynamical mass are extremely dependent on distance, which was the basis of some criticisms of the NGC 1052-DF2 discovery paper.
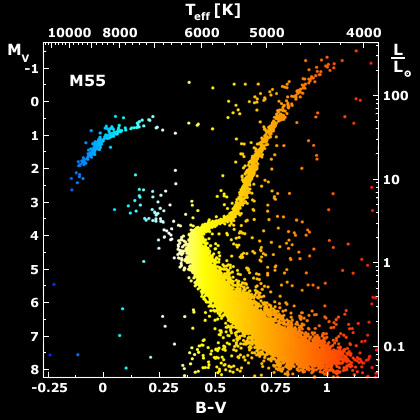
Tip of the Red Giant Branch (TRGB) stars (see Figure 1) are stars that have just run out of hydrogen and started to burn helium. Being at this turning point in their lives gives TRGB stars a characteristic brightness and color, meaning that they can be used to measure distances (like here). In this paper, members of the Dragonfly team use TRGB stars to measure the distance to NGC 1052-DF4, another seemingly dark matter-deficient galaxy.
Tipped Off (by) the Edge

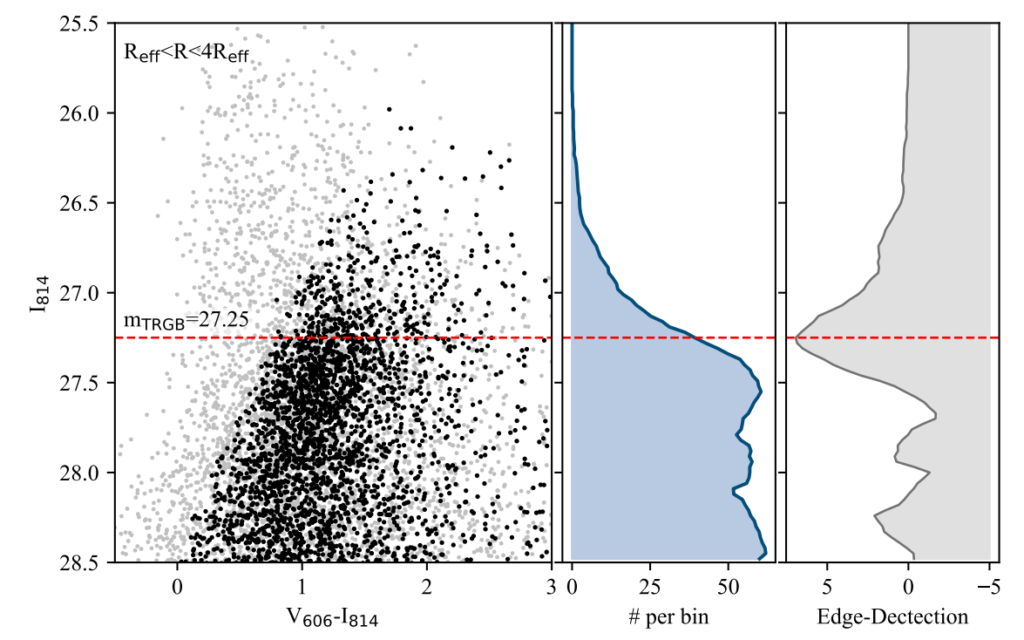
The authors base their study on observations taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (see Figure 2). To identify the TRGB stars, the authors first separate out RGB stars from the rest. They then group these RGB stars based on their brightness to get a luminosity function for the galaxy. The first derivative of the luminosity function is then used to identify where the location of the TRGB stars (see Figure 3). This technique is called edge-detection.
The identified location of the TRGB doesn’t seem to shift too much with radius, and pegs the apparent magnitude of TRGB stars (in the I814 band) at 27.25 ± 0.11 mag. The absolute magnitude of TRGB stars in the I814 band is about -4.0 mag. Taken with the apparent magnitude and median color of the identified TRGB stars, this gives a distance of 18.3 ± 1.0 megaparsecs (1 megaparsec ~ 3.26 million light years) to NGC 1052-DF4.
Not So Distant
To understand and account for photometric errors (which edge detection is unable to do), the authors inject artificial stars into their observations and recover them. The authors then re-estimate the galaxy distance by modeling the galaxy using parameters obtained from their observations. They get a TRGB apparent magnitude of 27.31 ± 0.03 ± 0.09 (the first error spans the central 68% of the magnitude likelihood and the second error comes from systematic uncertainty) and a distance of 18.8 ± 0.9 megaparsecs.
The distance to NGC 1052-DF4 the authors obtain agrees with the distance obtained via surface brightness fluctuations (how the brightness of a galaxy varies if you divided it into segments and compared them). However, their TRGB distance differs by varying degrees from TRGB distances obtained by other studies. The authors suggest that this might be due to non-TRGB stars being mistaken for TRGB stars.
The TRGB distance obtained in this work places NGC 1052-DF4 in close proximity to NGC 1052 and NGC 1052-DF2, consistent with previous measurements. It also supports the interpretation that NGC 1052-DF4 is a dark matter-deficient galaxy. NGC 1052-DF2 will receive similar treatment very soon, continuing the fascinating story of these strange galaxies.




